Neuroendocrine tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) present complex challenges for patients, including delays in diagnosis, which can lead to years of frustration. As part of our commitment to Find, Fight and Follow® disease, we’re dedicated to addressing the unmet needs associated with this difficult-to-identify and hard-to-treat cancer.
Understanding NETs
NETs can grow slowly and arise when neuroendocrine cells begin to divide uncontrollably and form a tumor, which may be due to DNA mutations.1 Neuroendocrine cells, which produce and secrete hormones in response to signals from the nervous system, can be found throughout the body, meaning NETs can vary widely in location, type and spread.
At Lantheus, we are focused on NETs located throughout the body, including a subset specifically found in the pancreas and digestive system called gastroenteropancreatic NETs (GEP-NETs).
GEP-NETs are grouped into two categories
GEP-NETs are either functional, meaning they produce extra hormones that lead to hormone-related symptoms, or nonfunctional, meaning they do not produce any extra hormones or hormone-related symptoms.
Clinical challenges with GEP-NETs
With symptoms2 ranging from fatigue and nausea to abdominal pain, GEP-NETs diagnosis can be difficult and is often delayed. While the increasing incidence of GEP-NETs may reflect diagnostic improvements, ongoing challenges in detection may contribute to low survival rates, especially in metastatic cases.3
Signs and symptoms
Nausea
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain
Tiredness
Unintended weight loss
Flushing or redness
of the skin
of GEP-NETs are misdiagnosed, leading to delays in care4
years is the median delay from symptoms to GEP-NET diagnosis5
Our approach
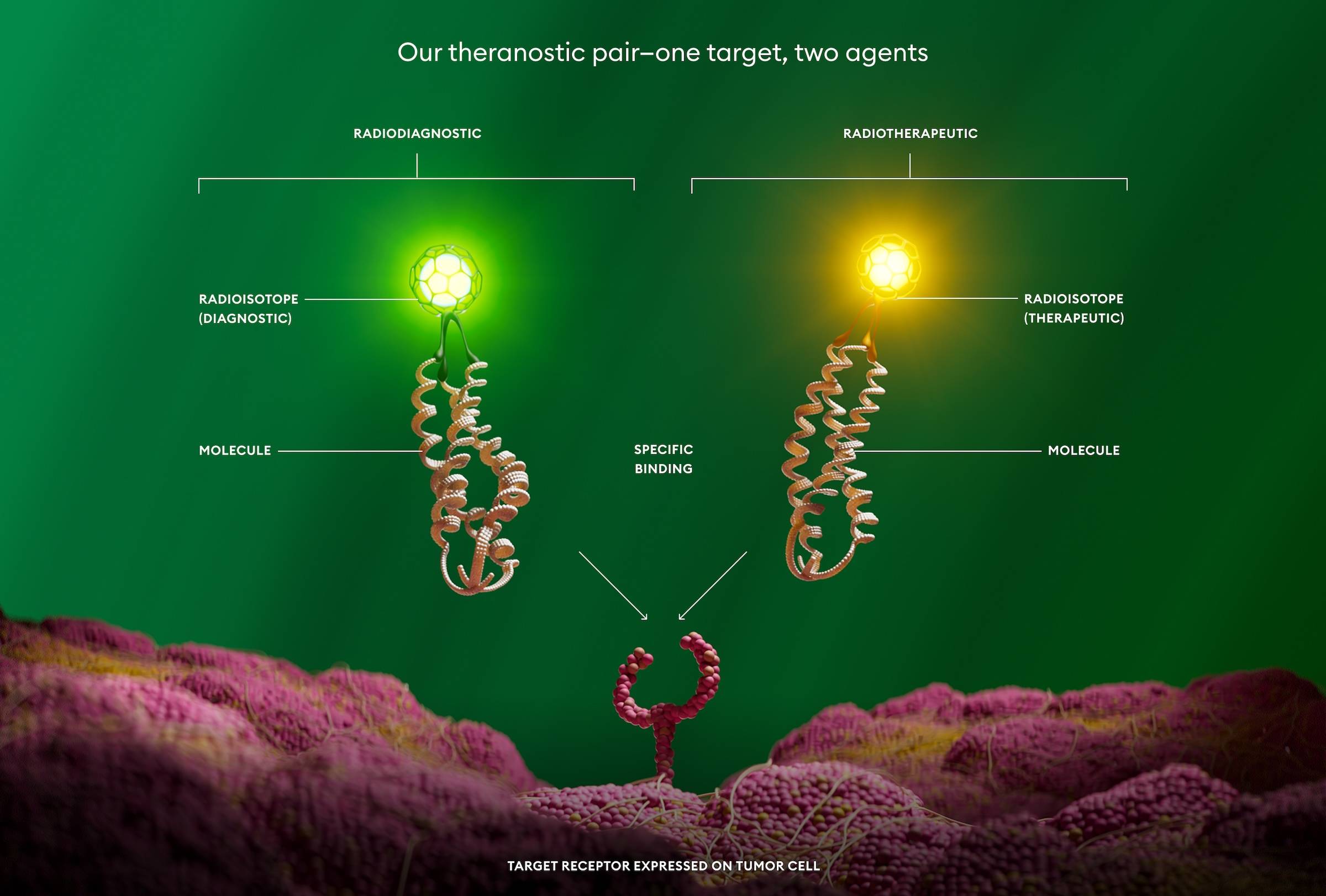
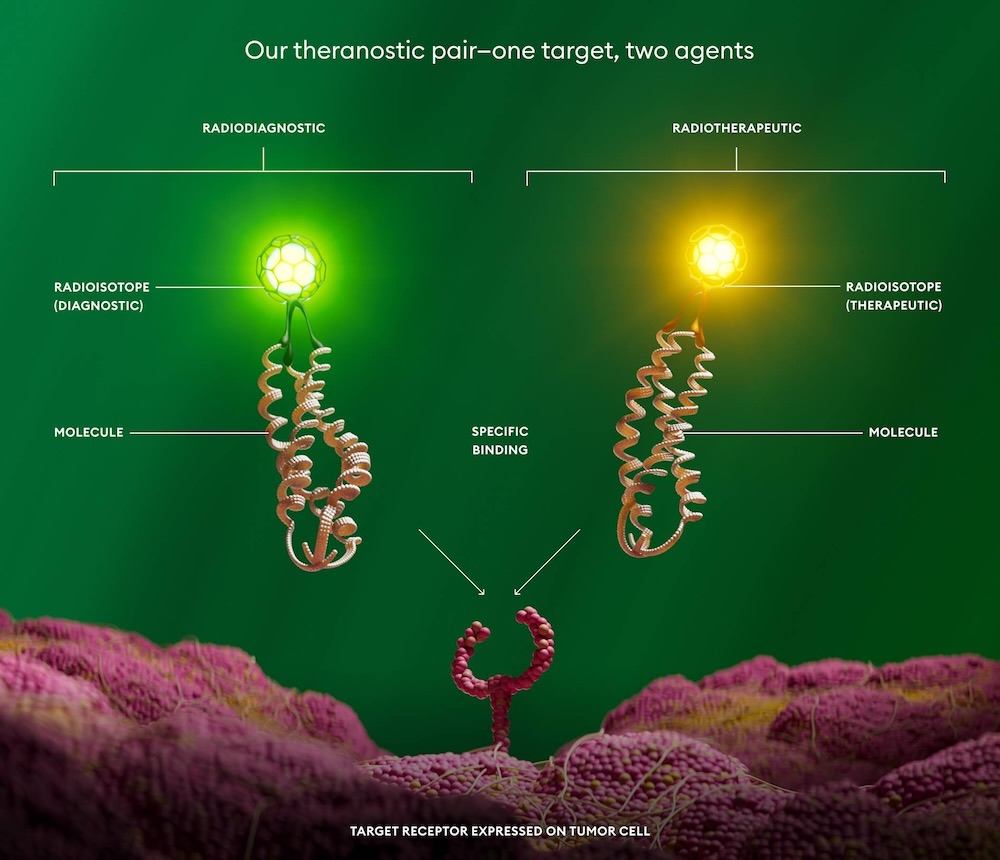
Lantheus is developing a theranostic approach for GEP-NETs which involves investigating a radiodiagnostic agent to detect SSTR+ NETs using positron emission tomography (PET) for staging and localization, along with a radiotherapeutic candidate for their treatment.
Our theranostic pair: one target, two agents
REFERENCES
1. Neuroendocrine Tumors. Cleveland Clinic. Published June 26, 2024. Accessed May 22, 2025. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22006-neuroendocrine-tumors-net 2. Neuroendocrine Tumors. Mayo Clinic. Accessed May 22, 2025. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/neuroendocrine-tumors/symptoms-causes/syc-20354132 3. Epidemiology, Incidence, and Prevalence of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Are There Global Differences? National Library of Medicine. Published March 14, 2021. Accessed May 22, 2025. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8118193/ 4. P-136 Survey of Challenges in Access to Diagnostics and Treatment for Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients (SCAN): Early Diagnosis and Treatment Availability. Annals of Oncology. Published July 2020. Accessed May 22, 2025. https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(20)39517-X/fulltext 5. Principles of Diagnosis and Management of Neuroendocrine Tumours. National Library of Medicine. Published March 13, 2017. Accessed May 22, 2025. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5359105/